The article discusses Apple’s App Store policies in the context of current technological shifts such as the rise of generative AI and the legal challenges posed by the EU’s Digital Markets Act (DMA). It explores the tension between Apple’s control of its ecosystem, which has benefited many, and the negative consequences of such control. Furthermore, it highlights the complexities and dilemmas the EU faces in implementing the DMA to balance competition and user safety, without compromising the security and reliability of Apple’s platform.
Main Points
Generative AI is central to tech innovation.
Generative AI, not smartphone apps, is now at the forefront of tech innovation.
EU's DMA presents legal challenges for Apple.
The Digital Markets Act (DMA) by the EU aims to force significant changes in Apple’s App Store policies.
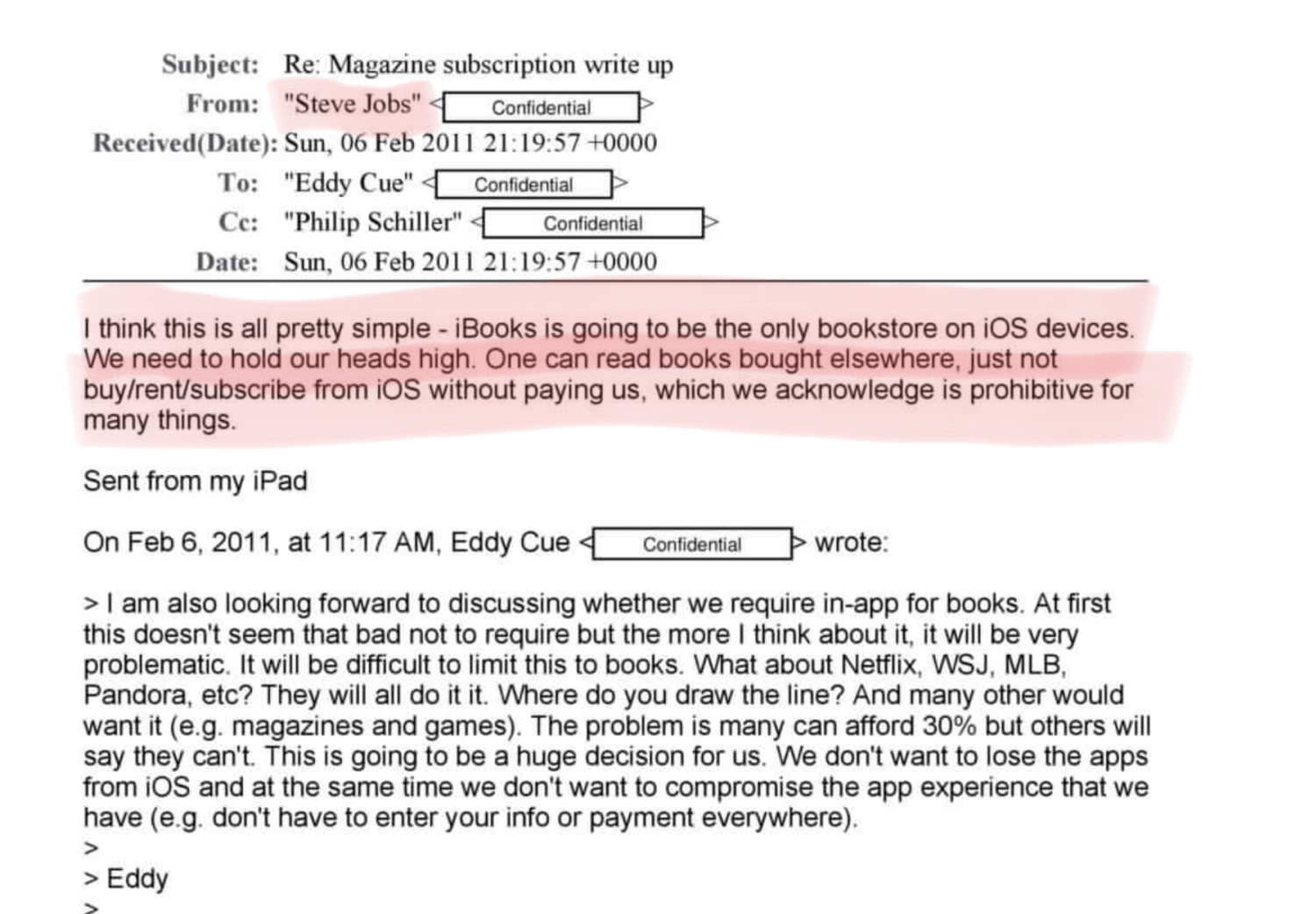
Apple's control has mixed consequences.
While Apple’s ecosystem benefits most stakeholders, its control can also negatively impact users and developers.
EU faces dilemma with DMA implementation.
The DMA’s implementation poses a dilemma as it seeks to balance competition and user safety within Apple’s ecosystem.
Insights
Generative AI is now central to tech innovation.
The world has moved on from smartphone apps to generative AI as the centre of tech innovation, excitement, and company creation.
The EU's Digital Markets Act (DMA) introduces significant legal challenges for Apple.
With the DMA, the EU tells Apple it must change its App Store policies, adding to the pressures from a USA court ruling and potential DoJ/FTC lawsuit.
Apple's control of its ecosystem has mixed consequences.
Apple’s managed system benefits most developers, users, and itself, but its control sometimes harms users and developers for Apple’s own benefit.
The EU faces a dilemma with the DMA's implementation.
The DMA tries to navigate the trade-off between competition and user safety but demands Apple to open its ecosystem without compromising security and reliability, leading to complex challenges.