-
Ibis represents a significant shift in the realm of online encyclopedias, introducing a federated model using the ActivityPub protocol to decentralize knowledge storage and sharing. Developed by Felix “nutomic” Ableitner, Ibis aims to solve the inherent vulnerabilities and trust issues plagued by Wikipedia and similar centralized platforms. With core functionalities demonstrated in a proof of concept, Ibis has the potential to foster a network of interconnected, specialized knowledge bases, offering diverse and reliable information across various topics.
Main Points- Wikipedia scandalsWikipedia has been embroiled in numerous scandals, diminishing its credibility.
- Need for decentralized knowledge platformsCentralized knowledge repositories are susceptible to corruption, highlighting the need for decentralized alternatives.
- Introduction of IbisIbis leverages federated technology to create a distributed encyclopedia, showcasing a proof of concept with major functionalities.
- Potential of federated modelIbis's federated model allows for diverse, specialized instances, transforming the landscape of online encyclopedias.
122004763 -
Daytona, the Open Source Development Environment Manager, offers a streamlined process for setting up development environments with a single command. It supports various infrastructure and integrates multiple features like Git provider connections, IDE support, configurations, and security, making the setup process simpler and more efficient.
Main Points- Single Command SetupDaytona enables the activation of a fully configured development environment with a single command.
- Runs EverywhereDaytona supports development on local, remote, cloud-based, physical servers, or VMs across any architecture (x86 or ARM).
- Git Provider IntegrationDaytona supports integration with major Git providers like GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, and Gitea.
122004763 -
Mostr bridge uptime shows the status of the bridge between ActivityPub and Nostr. This open source project is powered by Upptime.
Main Points- Bridge between ActivityPub and NostrMostr Bridge is an uptime status page for the bridge between ActivityPub and Nostr.
- Page is open sourceThe page is open source and is powered by the project Upptime.
122004763 -
Open-source geocoding platform Nominatim enables users to find places by name or address and look up addresses for a given location using latitude and longitude. It supports free-form queries in any language and a structured query mode for automating geocoding of extensive address lists. It also allows finding the nearest address for any latitude and longitude or any OSM object given its ID.
Main Points- Find places by name or address (Geocoding)Nominatim can power the search box on your website, allowing your users to type free-form queries (“Cafe Paris, New York”) in any language. It also offers a structured query mode (“postcode=12345”, “city=London”, “type=cafe”) that helps you to automate geocoding of extensive address lists.
- Look up addresses for a location (Reverse geocoding)Given a latitude and longitude anywhere on the planet, Nominatim can find the nearest address. It can do the same for any OSM object given its ID.
122004763 -
GitHub - pretzelai/pretzelai: Open-source, browser-local data exploration using DuckDB-Wasm and PRQL (github.com)
Pretzel is an open-source, offline browser-based tool for data exploration and visualization, leveraging WebAssembly-based DuckDB and PRQL for performance, with privacy-first design.
122004763 -
“Algorithms for Modern Hardware” is an upcoming high-performance computing book by Sergey Slotin, aimed at a wide range of readers from performance engineers to undergraduate students. The book, hosted entirely on GitHub, focuses on using modern hardware’s parallelism capabilities for practical algorithm speed improvements. It is divided into various parts, with themes ranging from performance engineering to distributed computing, and encourages community contributions and feedback.
Main Points- Performance EngineeringThe book covers the basics of computer architecture and optimization of single-threaded algorithms, detailing CPU optimization topics like caching, SIMD, and pipelining.
- Parallel AlgorithmsAddresses concurrency, cache coherence, synchronization primitives, OpenMP, and more, focusing on models of parallelism and concurrent algorithms.
- Distributed ComputingExplores distributed computing topics like networking, message passing, distributed databases, and cloud computing.
- Software & HardwareCovers software and hardware aspects like LLVM IR, compiler optimizations, FPGAs, ASICs, TPUs, and other AI accelerators.
122004763 -
LaVague is an innovative project that automates menial, repetitive tasks on the internet by transforming natural language instructions into Selenium code, allowing users to focus on more meaningful endeavors. It leverages open-source models and advanced AI techniques to ensure user control and privacy. The project is in its early stages but has the potential to democratize transparent and aligned AI models.
Main Points- Efficient Browser AutomationLaVague offers natural language processing and Selenium integration for efficient browser automation.
- Open-Source and TransparentBuilt on open-source projects, ensuring transparency and alignment with user interests.
- Advanced AI TechniquesSupports advanced AI techniques for optimal action selection without code generation fine-tuning.
- Democratizing AIProject aims to democratize transparent and aligned AI models for Internet users.
122004763 -
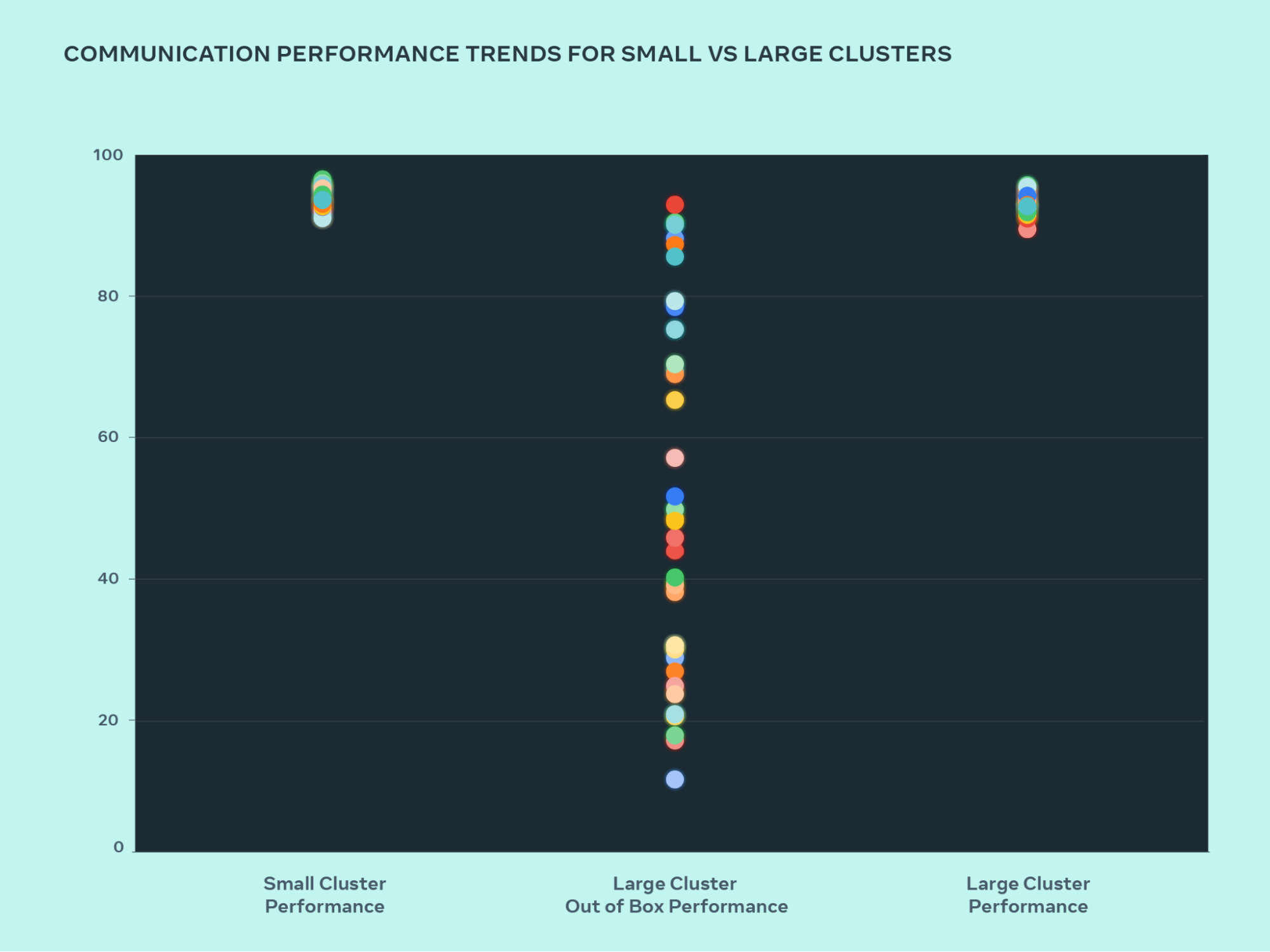
AI Meta GPU Clusters Open Source Infrastructure AI and Machine Learning Technology Artificial Intelligence
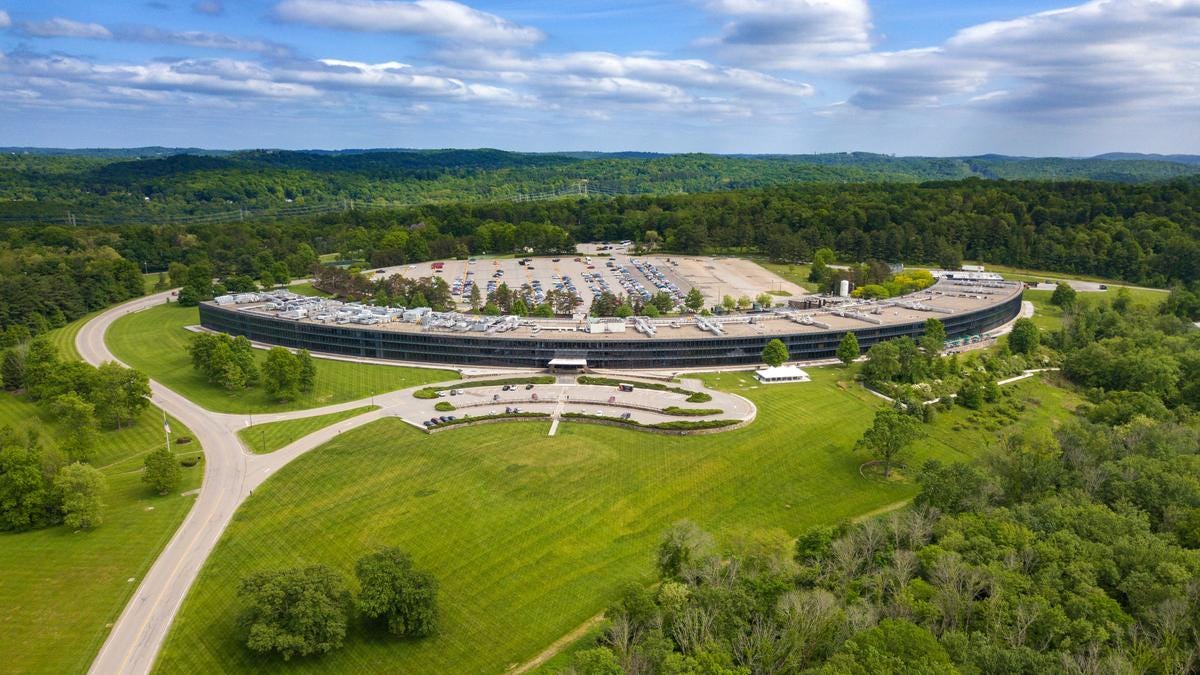
Meta announces the construction of two 24k GPU clusters as a significant investment in its AI future, emphasizing its commitment to open compute, open source, and a forward-looking infrastructure roadmap aimed at expanding its compute power significantly by 2024. The clusters support current and future AI models, including Llama 3, and are built using technologies such as Grand Teton, OpenRack, and PyTorch.
Main Points- Meta announces two 24k GPU clusters for AI workloads, including Llama 3 trainingMarking a major investment in Meta's AI future, we are announcing two 24k GPU clusters. We are sharing details on the hardware, network, storage, design, performance, and software that help us extract high throughput and reliability for various AI workloads. We use this cluster design for Llama 3 training.
- Commitment to open compute and open source with Grand Teton, OpenRack, and PyTorchWe are strongly committed to open compute and open source. We built these clusters on top of Grand Teton, OpenRack, and PyTorch and continue to push open innovation across the industry.
- Meta's roadmap includes expanding AI infrastructure to 350,000 NVIDIA H100 GPUs by 2024This announcement is one step in our ambitious infrastructure roadmap. By the end of 2024, we’re aiming to continue to grow our infrastructure build-out that will include 350,000 NVIDIA H100 GPUs as part of a portfolio that will feature compute power equivalent to nearly 600,000 H100s.
122004763 -
The Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD) history outlines the evolution of UNIX from its first public presentation in 1973, through legal and technical challenges faced by AT&T and early adopters, to its spread across academia and development into a widely influential open-source operating system. This pathway highlights key moments such as the first UNIX port outside of PDP-11 to IBM 360, the creation and distribution of BSD leading to significant advancements in operating systems, and the eventual wide-reaching impact of BSD on modern computing, including the development of macOS, NetBSD, OpenBSD, FreeBSD, and others.
Main Points- Public presentation of UNIX.Initial public presentation of UNIX in 1973 received polite but subdued reaction.
- AT&T's legal issues with distributing UNIX.AT&T faced potential legal issues in distributing UNIX due to its monopoly position.
- UNIX port to IBM 360.The successful port to IBM 360 marked UNIX's adaptability to varied hardware.
- BSD's impact on modern operating systems.Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD)'s significant contributions to operating system development, leading to the creation of many modern OSes.
122004763
We can't find the internet
Attempting to reconnect
Something went wrong!
Hang in there while we get back on track

Tags
see all- Technology
- AI
- Open Source
- programming
- AI and Machine Learning
- Elixir
- Artificial Intelligence
- philosophy
- Personal Growth
- Rust
- business
- social change
- software development
- Python
- machine learning
- innovation
- Linux
- DIY
- collaboration
- Nominatim
- architecture
- Entertainment
- performance improvement
- performance
- education
- Android
- PostgreSQL
- Docker
- Deadspin
- ActivityPub
- Slint
- Developer Experience
- NixOS
- SQL
- Drone
- neural networks
- simulation
- Erlang
- Journalism
- Entrepreneurship
- LLM
- scalability
- Concurrency
- fault tolerance
- immutable URLs
- Nix
- productivity
- WebAssembly
- Database
- Generative AI
- Security
- Home Lab
- deployment
- ESP32
- Language Models
- automation
- Data Visualization
- Markets
- Networking
- Ecto
- computing
- BEAM
- metal recovery
- Quantum Computing
- Robotics
- Web 2.0
- financial wellbeing
- harsh environments
- Miniaturization
- eclipse safety
- Public Health
- Web PKI
- Chess
- Transparency
- memory allocation
- safety
- brinespace
- Diversity
- brewer's yeast
- hardware review
- Cryptanalysis
- compiler backend
- anterior neostriatum
- compression
- Psychology
- Vulnerabilities
- computational complexity
- luxury
- Windows
- Natural Language Processing
- cloud native
- Legal Battle
- maintainability
- Lifestyle
- US Jobs Market
- Mike Benz
- dinosaurs
- Investment Strategy
- Xerox Park
- design
- Bletchley Park
- gaming
- Consumer Advice
- AI Democratization
- Economy
- Behavioral Biology
- Particles
- Parallelism
- brain abnormalities
- Query Optimization
- Church Growth
- Mathematics
- WWII
- problem-solving
- Cerebras Systems
- structured inference
- API
- LaVague
- mechanical design
- UNIX
- Certificate Transparency
- Ericsson
- Iman Gadzhi
- Thermodynamic Computing
- Nvidia
- electrolyte solutions
- setup simplicity
- Synchronization Primitives
- Wasmtime
- work-life balance
- Big Tech
- LLMs
- Twitch
- Tucker Carlson
- Garbage Collection
- machining
- Personal Reflection
- free speech
- Generosity
- Sports Stadiums
- Ash 3.0
- WebTransport
- celestial event
- ChatGPT
- processor-controlled
- computer graphics
- Actor model
- oral rehydration solution
- Missouri v. Biden
- password security
- Academic Freedom
- developer tools
- capitalism
- compilation
- total solar eclipse
- Performance Engineering
- Effective Methods
- 3D printing
- Wi-Fi Control
- hardware-controlled
- S&P 500
- Telemetry
- Encoding
- Theology
- First Amendment
- ISO GQL
- Web Monitoring
- Data Compression
- development environment management
- intelligence agencies
- Satire
- Divine Healing
- NSA
- WSE-3
- corporate media
- YouTube
- Project Management
- Sunlight
- basal ganglia
- constraints
- Online Learning
- Mobile App Development
- Medical Technology
- teamwork
- Server Management
- High-Performance Computing
- aviation
- Hugo Barra
- processes
- GUI Toolkit
- Foreign Data Wrapper
- Debugging
- spiritual experience
- indie game development
- kernel exploitation
- note-taking
- Cost-saving
- biosorption
- shuffle
- Probabilistic Machine Learning
- Economic Trends
- Media Criticism
- CMOS integrated circuits
- GPU security
- Technology Criticism
- health benefits
- Upptime
- Flutter
- Jensen Huang
- copyright
- Logging
- Memory Tagging Extension
- streaming service
- undecidability
- Enigma
- Speculative Execution
- remote work
- Coding
- Social Responsibility
- Corporate Profits
- Adm. Hyman G. Rickover
- Cipher
- Stable Video 3D
- AI Chip
- Nostr
- boot sequence
- APIs
- Pixel 8
- management
- register allocation
- Jordan Peterson
- Non-Transformer Models
- NewsGuard
- Computer Systems Research
- Content Creation
- system administration
- navy
- Software Support
- nuclear submarine
- Veeps
- Elisp
- StashPad Docs
- Truth
- Pentecostal Movement
- Categorical Thinking
- Deglobalization
- live sports
- Annual Letter
- cholera
- GitHub Actions
- Vaccine Mandates
- Flox
- devops
- Containerization
- E-graphs
- NP class
- Data Contamination
- Function Calling
- table formatting
- treatment
- Internet Iron Curtain
- Extropic
- AR
- Ovid
- development
- Federated System
- National Science Foundation
- Operating Systems
- functional programming
- Cypher
- JIT Compiler
- community discourse
- virtual environment
- Nostalgia
- RISC
- time management
- WebRTC
- Microsoft Research
- CIA
- AMD Graphics Cards
- Murthy v. Missouri
- superoptimization
- Geocoding
- GUI
- package manager
- Chips
- Evangelism
- low-cost project
- Wikipedia
- mammals
- communication
- Standards
- library
- OpenAI
- Selenium
- weight loss
- workplace culture
- Cranelift
- diagnosis
- pattern-matching
- troubleshooting
- Handheld Devices
- Circuit Digest
- Statistical Analysis
- AppSignal
- Parallel Computing
- titanosaurs
- spy agencies
- Meta
- The New York Times
- Torsion Springs
- Deep Packet Inspection
- leadership
- Growth
- OpenStreetMap
- Zed
- Ollama
- Let's Encrypt
- Richard Stallman
- GPU Clusters
- life advice
- Garnet
- software failure
- COVID-19
- LiveView
- Turing Machines
- federated models
- operating system
- GPUI
- Long-Polling
- text renderer
- software
- flash memory
- message passing
- AI-driven development
- Genetics
- community building
- schema migration
- cache-store
- Live-Preview
- evaluation
- BSD
- real-time communication
- software engineering
- video games
- hoaxes
- Church-Turing Thesis
- Algorithm
- Human Behavior
- workflows
- conditional
- Log-Normal Distribution
- CRDT
- AI Supercomputers
- Tablex
- FBI
- Garage Door Repair
- TypeScript
- Technology Trends
- Software Release
- pcase
- e-waste management
- N-channel diamond MOSFET
- Hollywood
- Lockdowns
- reptiles
- coding environment
- asynchronous communication
- Emacs
- Uppttime
- biometrics
- Financial Woes
- Blackwell
- 3D generation
- Learning Curve
- computational models
- Structured Logging
- Berkeley
- Server-Sent Events
- Race Conditions
- The Jet Business
- misinformation
- Stashpad
- Customization
- bitfield
- software critique
- Stability AI
- reinforcement learning
- VIBES
- immersive technology
- UI development
- Fingerprinting
- In-Context Learning
- scaling
- SIMA
- Regression Analysis
- Techno-Optimism
- Algorithm Design
- AT&T
- AI Acceleration
- Domain Modeling
- RP2040
- incident commander
- Personal Pronouns
- Ultrasound
- OpenVPN
- diamond electronics
- Hardware Selection
- theoretical computer science
- Notifications
- dehydration
- execution plan
- CVE-2023-6241
- animal behavior
- Google Docs alternative
- macOS
- Patience
- developmental language disorder
- Culture
- Johnny Depp
- hash table
- Sports
- browser automation
- Vision Pro
- nuclear navy
- authentication
- Database Innovation
- knowledge sharing
- Technology History
- virtual reality
- Xerox PARC
- UI/UX Design
- Transition
- WebSockets
- VS Code
- Computer Science
- cryptography
- .NET
- Daytona
- Android security
- Optimization
- PRQL
- Servers
- media bias
- Neovim
- VPN
- code-generation
- Design Systems
- censorship
- user code execution
- Capabilities
- Queries
- game design
- randomness
- x86
- Wafer Scale Engine 3
- lawsuit
- Source Code
- AI agent
- private jet
- PCB design
- Redis
- graph theory
- system design
- Abundance
- Cybersecurity
- sustainable technology
- Tools Format
- Phoenix
- system efficiency
- MEMS
- Decision Table
- Alan Kay
- Public Image
- Management Disputes
- computer vision
- Graph Database
- cond*
- Infrastructure
- Encyclopedia
- VR
- ARPA
- web development
- Apple
- Hermes-2-Pro-Mistral-7B
- DuckDB
- Unison
- disinformation
- sauropod
- Computability
- Feature Learning